Neurological Signal Compression
Signal Compression for High-Density ECoG Arrays
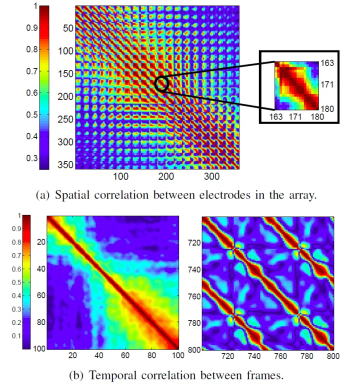
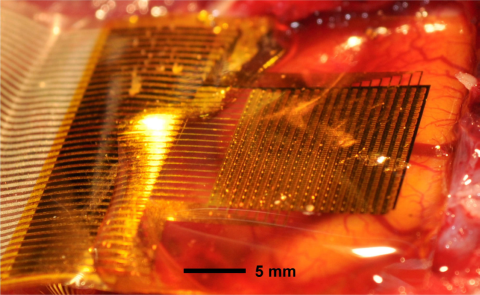
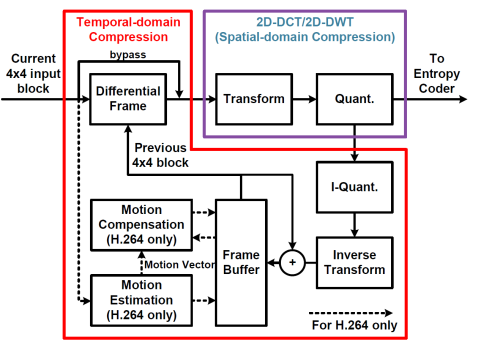
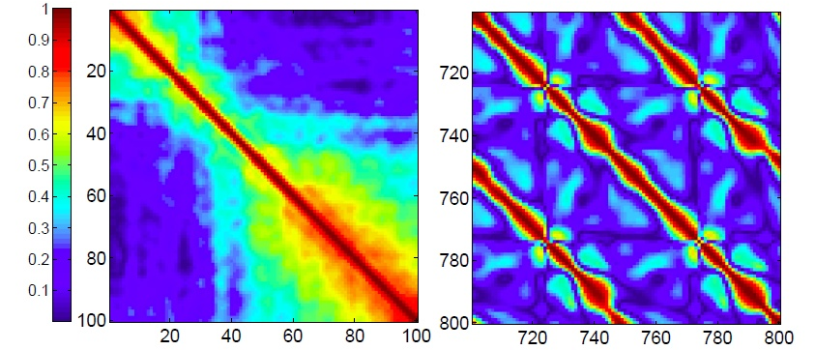
High-resolution Electrocorticography (HR-ECoG) emerged as an enabling technology to provide unprecedented temporal and spatial resolution for applications such as brain-computer interfaces (BCI), seizure detection for epilepsy and basic neuroscience. The 400x higher resolution of HR-ECoG compared to the conventional ECoG challenges the processing, transmission and storage technologies. For practical HR-ECoG-based portable or implantable devices, there is a clear need for highly-efficient compression algorithms with very low power requirements. Our work in this project focuses on analysis of the HR-ECoG characteristic to identify and design such compression algorithms. In our studies, we show that HR-ECoG signals have both high spatial and temporal correlations similar to video/image signals. In light of this observation, we are designing various compression algorithms based on video/image–compression techniques such as motion estimation, discrete cosine transform (DCT) and discrete wavelet transform (DWT).
Low-Power EEG Compression
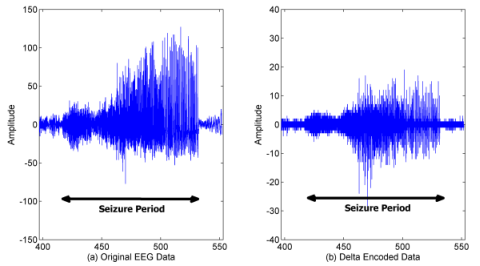
Compression is usually considered as an auxiliary task to reduce data bandwidth without interacting with the main functionality of a device. For instance, for wireless seizure monitoring devices seizure detection and data compression are usually considered separately, where data is compressed before or after the seizure detection. As a result, the algorithms for these two tasks are usually developed and deployed separately. Since, battery life has prime importance for implantable devices, combining such functionality using a single low-power algorithm to achieve both tasks is desirable. Our goal in this project, as exemplified in this seizure monitoring device case, is to develop compression algorithms with dual purposes to increase the overall power-efficiency of the devices. The broader goal of the project is to develop techniques to integrate the compression into the core of the algorithm development for applications (such as seizure detection) from the beginning of the design cycle and by doing so allow optimization that takes advantage of this combination.
Selected Related Publications
- C.-L. Sha, T. Kim, N. Sertac Artan, and H. J. Chao, “Compression-Ratio-Based Seizure Detection,” in 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2013), Osaka, Japan, Jul. 2013. [ bib | pdf ]
- T. Kim, N. Sertac Artan, J. Viventi, and H. J. Chao, “Spatiotemporal Compression for Efficient Storage and Transmission of High-Resolution Electrocorticography Data,” in 34th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2012), San Diego, CA, Aug-Sep 2012. [ bib | pdf ]