Spike Detection for Extracellular Recordings
Robust Spike Detection for High Firing Rate and Low SNR
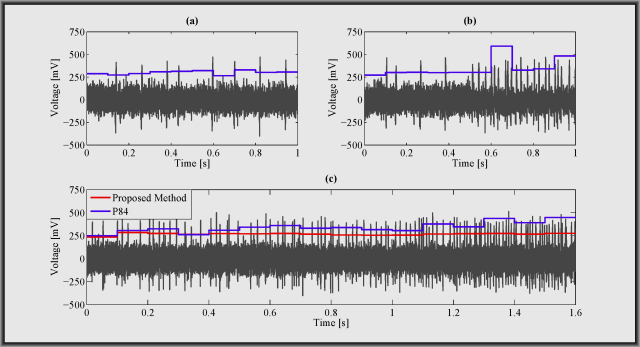
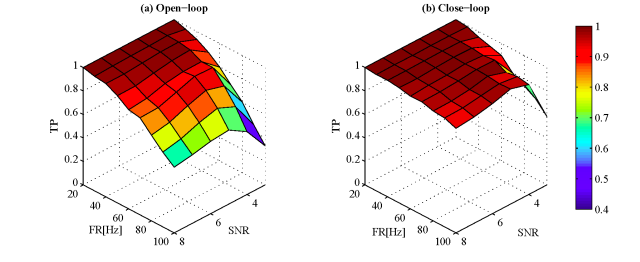
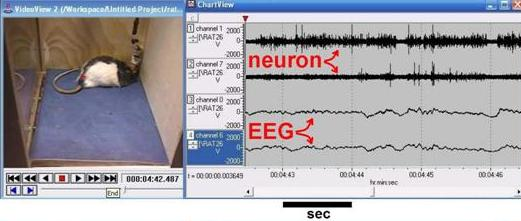
Extracellular Spike detection is at the core of most brain-computer interfaces (BCI) and has applications in other areas such as epileptic seizure detection. Inaccurate spike detection can impair all the higher level processing. Depending on the application the spike detectors should be able to operate at a wide range of parameter variability. For instance, firing rates and signal-to-noise ratio can vary with time. In this project, we develop spike detection techniques that are robust against parameter variability by utilizing feedback mechanisms between spike detection, sorting and noise level estimation. We also investigate feedback mechanisms between the digital processing circuits to analog front-end circuits.
Selected Related Publications
- N. Sertac Artan, X. Xu, and H. J. Chao, “A Low-Cost Reliable Online Noise Level Estimation For Accurate Spike Detection in Extracellular Recordings,” in IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS 2012), Hsinchu, Taiwan, Nov. 2012. [ bib | pdf ]
- N. Ludvig, H. M. Tang, N. Sertac Artan, P. Mirowski, G. Medveczky, S. L. Baptiste, S. Darisi, R. I. Kuzniecky, O. Devinsky, and J. A. French, “Transmeningeal Muscimol Can Prevent Focal EEG Seizures in the Rat Neocortex Without Stopping Multineuronal Activity in The Treated Area,” Brain Research, vol. 1385, pp. 182-191, Apr. 2011. [ bib ]
- N. Sertac Artan, P. Mirowski, H. Tang, G. Medveczky, S. Baptiste, H. J. Chao, O. Devinsky, R. Kuzniecky, and N. Ludvig, “Detecting Abnormally Large-Amplitude Multi-Neuron Bursts Before Focal Neocortical EEG Seizure Onset In Freely Behaving Rats,” Epilepsia, vol. 50, p. 391, Mar. 2009.[ bib ]